Body Cavities
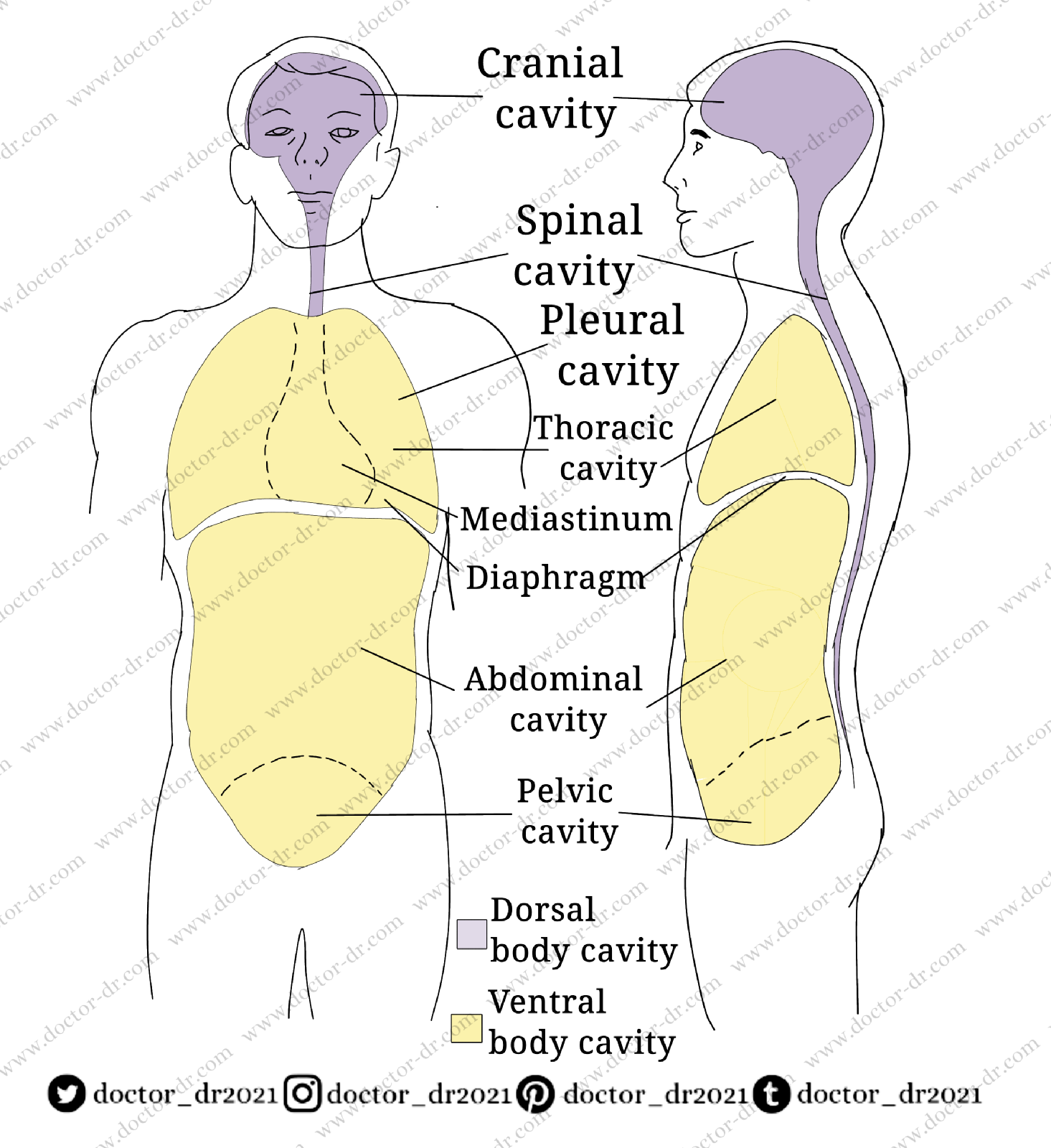
FIGURE 1-13 Body cavities. Location and subdivisions of the major body cavities.
Contrary to popular belief, the human body is not a solid structure. It is split into two main chambers, each of which includes compact, well-ordered groupings of internal organs. The ventral and dorsal body cavities are the two main cavities.
Figure 1-13 depicts the location and contours of the bodily cavities. The thoracic or chest cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity make up the ventral cavity.
A right and left pleural cavities, as well as a midportion known as the mediastinum, make up the thoracic cavity. The mediastinum is completely separated from the right pleural cavity, which houses the right lung, and the left pleural cavity, which houses the left lung. Fibrous tissue forms a wall around the mediastinum, completely separating it from the right pleural cavity, which houses the right lung, and the left pleural cavity, which houses the left lung. The lungs are the only organs in the thoracic cavity that are not in the mediastinum.
The heart (contained in its pericardial chamber), the trachea and right and left bronchi, the oesophagus, the thymus, different blood arteries (e.g., thoracic aorta, superior vena cava), the thoracic duct and other lymphatic vessels, various lymph nodes, and nerves are all found in the mediastinum (such as the phrenic and vagus nerves).
The abdominal cavity is the top section of the abdominopelvic cavity, while the pelvic cavity is the bottom portion. The liver, gallbladder, stomach, pancreas, intestines, spleen, kidneys, and ureters are all found in the abdominal cavity.
In the pelvic cavity, the bladder, some reproductive organs (uterus, uterine tubes, and ovaries in women; prostate gland, seminal vesicles, and part of the vas deferens in men), and a portion of the large intestine (particularly the sigmoid colon and rectum). The cranial and spinal cavities make up the dorsal cavity.
The brain is housed in the canial cavity of the skull. The spinal cord is housed in the spinal cavity, which is located in the spinal column (Figure 1-13).
Special names have been given to the thin filmy membranes that border body cavities or cover the surface of organs within body cavities. The actual wall of a bodily cavity or the lining membrane that covers its surface are both referred to as parietal. Visceral refers to the thin membrane that protects the organs, or viscera, within a cavity, rather than the hollow's wall or lining. the diaphragm disunites the thoracic and the abdominopelvic cavities
the bladder is located in body cavity
the heart is located in body cavity
the pleural cavity is the space
the urinary bladder is located in which body cavity
the liver is located in which body cavity
The parietal peritoneum, for example, is the membrane that lines the interior of the abdominal cavity. The visceral peritoneum is the membrane that protects the organs within the abdominal cavity. There is a gap or opening between the two membranes of the abdomen. The peritoneal cavity is the name for this area.