The proper operation of all the organs and blood arteries is crucial in a system as complicated as the circulatory system. This entails controlling the heartbeat's frequency and the blood's force as it passes through the veins.
Heartbeat and the Pacemaker
Your nervous system controls how quickly your heart beats. The pacemaker control centre is located behind the right atrium. Every pulse is initiated by the pacemaker, a microscopic collection of nerve and muscle cells. This tissue causes the cardiac muscle's nerve fibres to rapidly transmit neurological signals. The impulses go to the left atrium from the bottom up. The impulses cause another mass of nerve tissue to contract between the ventricles, sending impulses to the ventricles' outer walls. The atria can contract first because to this arrangement. As a result of the ventricles contracting, blood is forced into the arteries.
The impulses instruct the heart to beat slowly when you are at rest. However, during exercise, your muscle cells send signals to your brain. These impulses alert the brain to the body's increased requirement for nutrition and oxygen. This message is transmitted from the brain to the heart via the pacemaker. The speed of the heartbeat causes the body's blood to circulate more quickly. In this manner, the pacemaker, which maintains the heart pumping automatically, quickens or slows down in response to the demands of the body.
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is the amount of pressure that blood exerts on the vessel walls as it circulates through the body. The system may be under too much pressure if the force is too strong. The apparatus could be harmed.
A standard component of a physical examination is getting your blood pressure tested. Blood pressure in an artery is calculated as the force required to lift a column of mercury. Mg (millimetres of mercury) is the unit used to measure blood pressure.
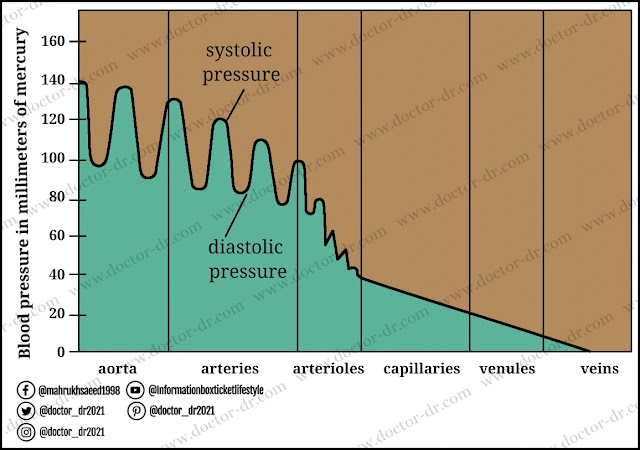
There are two different blood pressure measurements made. Systolic pressure is the first, while diastolic pressure is the second. The force of the blood pressing against the artery walls when the heart's ventricles contract is known as systolic pressure, or [sis TAHL ik]. In young adults, this is typically between 110 and 120 millimetres of Hg. Diastolic pressure, which is measured while the heart's ventricles are relaxed, is the force of the blood between beats. In young people, this typically ranges between 70 and 80 millimetres of Hg. The systolic reading is written over the diastolic reading when taking a blood pressure reading.
Within your circulatory system, your blood pressure varies from location to location. As your level of activity changes throughout the day, so does your blood pressure.
Heart Disorders and Diseases
When the heart cannot pump efficiently or the blood cannot flow smoothly, serious issues are likely to arise. There are many different types of heart disorders, including congenital heart disorders, rheumatic heart disease, hypertension, coronary heart disease, and heart attack.
Congenital Heart Disorders
Not everyone has a strong heart at birth. Congenital heart diseases are abnormalities in the way a baby's heart develops at birth. It's possible that the heart's blood flow control valves are malfunctioning. Between the two sides of the heart, there could be a hole. These conditions, among others, can inhibit development and activity or even result in mortality. Due to the heart's ongoing growth, certain problems resolve on their own. Surgery could be able to treat the problem in other situations.
Rheumatic Heart Disease
Rheumatic fever was until recently a prevalent cause of heart disease in children and young adults. Strep bacteria are the source of the illness known as rheumatic fever, which can cause muscle and heart valve inflammation. The heart valves may be scarred and damaged by this swelling. The injury might disrupt the heart's blood flow in the future, leading to rheumatic heart disease. A sore throat is frequently the first symptom of strep infection. Antibiotics are used to treat the first strep infection in order to avoid heart damage.
Hypertension
High blood pressure is also strongly linked to heart disease and stroke. High blood pressure is called hypertension. An increase in blood pressure is believed to be the result of a narrowing of the smaller blood vessels. Why this oc curs is not fully understood. But smoking, diet, stress, and heredity are all factors. The narrowing causes the heart to beat harder to pump the blood. A blood pressure of 140/90 represents border. line hypertension for adults. Higher pressure may be more serious.
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is the root cause of several other cardiac issues. Atherosclerosis is a disorder where fatty material accumulates on the walls of arteries and prevents blood flow. Cholesterol [kuh LES tuh rawl] makes up the majority of this fatty substance. if the obstruction is discovered in time. Both medication and surgery are options for treatment. The coronary blood flow will decline and harm the heart and arteries if the obstruction is not corrected. When the coronary arteries harden due to atherosclerosis, it results in coronary heart disease, also known as coronary artery disease. Everybody ought to have their cholesterol levels checked. A low-fat diet can help decrease a high level.
A heart attack may result from chronic coronary heart disease. An unexpected, potentially fatal occurrence known as a heart attack occurs when the heart muscles do not receive enough blood. Heart muscle deteriorates in some places. A heart attack strikes more than 1.5 million Americans each year.
Preventing Heart Disease
The top causes of death in the US are coronary heart disease and heart attacks. With a healthy diet, you can lessen your risk of acquiring certain cardiac issues. frequent physical activity and health screenings. Diet is very significant. It's crucial to stay away from meals that are heavy in animal fats and cholesterol. Consuming less salt can also be beneficial. Hypertension is a result of salt consumption and significantly raises heart attack risk. The prevention of heart disease depends heavily on regular exercise. The heart gets stronger with regular exercise since it is primarily formed of muscular tissue.
Lesson Review
The pacemaker and blood pressure are two ways your body regulates the heart and the circulatory system. There are many disorders that can affect the proper functioning of the heart. How- ever, exercise and a good diet can help the circulatory system function and prevent blockages that can lead to heart damage.
- Explain the function of the pacemaker.
- What are the two measurements of blood pressure?
- List three kinds of heart disorders.
- Explain how regular exercise can prevent heart disease.

~1.webp)

.webp)

