Introduction:
Artificial insemination (AI) is a groundbreaking technique that has revolutionized the fields of microbiology and biotechnology. By enabling controlled and efficient reproduction, AI has become an invaluable tool for enhancing agricultural productivity, preserving endangered species, and improving human reproductive technologies. In this article, we will explore the principles, applications, and advancements in artificial insemination, highlighting its significance for microbiology and biotechnology students.
1. Understanding Artificial Insemination:
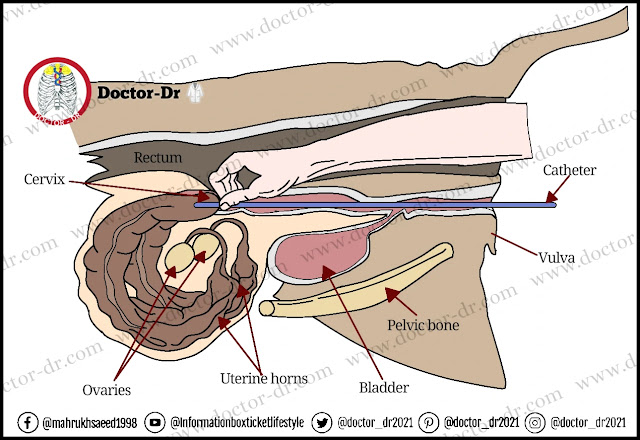
Artificial insemination refers to the deliberate introduction of semen into the reproductive tract of a female without natural mating. It involves the collection, processing, and transfer of semen to optimize successful fertilization. AI offers several advantages over natural mating, such as the ability to overcome geographical limitations, genetic improvement through selective breeding, and increased reproductive efficiency.
2. Applications of Artificial Insemination:
2.1. Agricultural Advancements:
AI has greatly transformed animal breeding in the agricultural industry. It allows the use of superior genetics by employing highly productive sires for semen collection and subsequent distribution to a larger number of females. This technique facilitates rapid and widespread genetic improvement, leading to increased milk and meat production, disease resistance, and overall productivity in livestock populations.
2.2. Conservation of Endangered Species:
Artificial insemination plays a critical role in conserving endangered species by maintaining genetic diversity and promoting successful reproduction. In situations where natural breeding is challenging due to small populations or behavioral issues, AI offers a viable solution. By collecting and storing semen samples from endangered species, scientists can artificially inseminate females to ensure the survival of these threatened populations.
2.3. Human Reproductive Technologies:
Artificial insemination is extensively employed in human reproductive technologies, such as assisted reproductive treatments (ART) and fertility preservation. In cases where couples face infertility issues, AI can be utilized to bypass certain reproductive barriers. Techniques like intrauterine insemination (IUI) and in vitro fertilization (IVF) involve the introduction of carefully processed and selected sperm samples into the female reproductive tract, increasing the chances of successful conception.
3. Advancements in Artificial Insemination Techniques:
3.1. Semen Processing and Storage:
Semen collection techniques have evolved significantly, ensuring the quality and viability of sperm samples. Semen processing involves the removal of debris, dilution, and cryopreservation, allowing long-term storage and transport. Cryopreservation techniques, including the use of liquid nitrogen, help preserve sperm viability for extended periods, ensuring the availability of high-quality genetic material.
3.2. Assisted Reproductive Technologies:
Advancements in biotechnology have led to the development of advanced assisted reproductive technologies, such as intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) and pre-implantation genetic testing (PGT). These techniques enhance the success rates of artificial insemination by improving sperm selection, genetic screening, and embryo development, thereby providing greater control and precision in the reproductive process.
4. Challenges and Ethical Considerations:
While artificial insemination has numerous benefits, it also poses certain challenges and ethical considerations. These include the potential loss of genetic diversity, the risk of inbreeding, and the need for responsible management of assisted reproductive technologies to ensure their ethical and sustainable use.
Conclusion:
Artificial insemination has transformed the fields of microbiology and biotechnology, providing unprecedented opportunities for genetic improvement, conservation, and human reproduction. Microbiology and biotechnology students play a crucial role in advancing this technology further, by exploring novel techniques, addressing challenges, and maintaining ethical practices. As the applications and advancements in artificial insemination continue to expand, its significance in microbiology and biotechnology will only continue to grow, fostering progress in various fields and benefiting both humans and the natural world.



.webp)

.webp)
