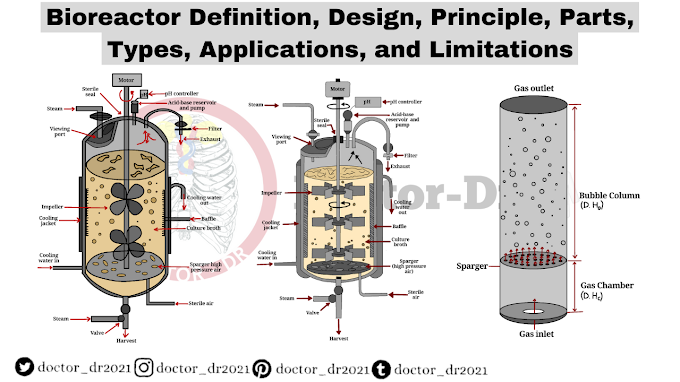
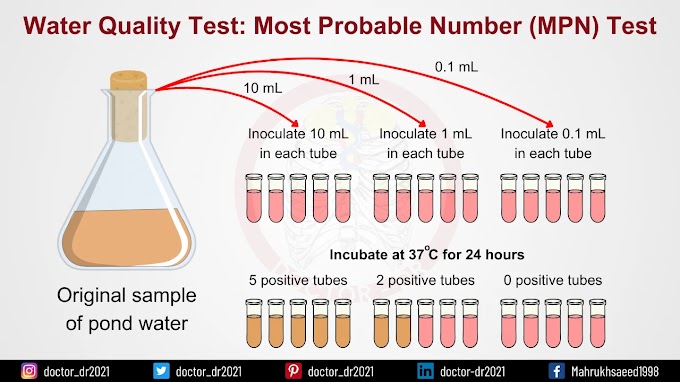
Introduction:
Bronchitis and bronchiolitis are two common respiratory conditions that affect the airways, causing inflammation and difficulty breathing. While they share similar names and affect the same region of the body, they are distinct conditions with different causes, symptoms, and treatments. Understanding the differences between bronchitis and bronchiolitis is crucial for proper diagnosis and management.
Bronchitis:
Definition:
Bronchitis refers to the inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which are the air passages that carry air to the lungs. It can be acute or chronic.
Causes:
Acute bronchitis is often caused by viral infections, such as the common cold or flu viruses. It can also be triggered by bacterial infections or irritants like smoke or air pollution. Chronic bronchitis is commonly associated with smoking and long-term exposure to irritants.
Symptoms:
Common symptoms of bronchitis include coughing, often with mucus, chest discomfort, fatigue, and mild fever. Acute bronchitis symptoms typically resolve within a few weeks, while chronic bronchitis symptoms may persist for months and recur over several years.
Treatment:
Treatment for acute bronchitis focuses on relieving symptoms and may include rest, hydration, over-the-counter pain relievers, and cough suppressants. Antibiotics are not effective against viral infections but may be prescribed if a bacterial infection is present. For chronic bronchitis, quitting smoking and avoiding lung irritants are essential, along with medications to manage symptoms and improve lung function.
Bronchiolitis:
Definition:
Bronchiolitis is a common respiratory infection that primarily affects infants and young children. It causes inflammation and congestion in the smallest air passages of the lungs, known as bronchioles.
Causes:
Bronchiolitis is most commonly caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), although other viruses such as rhinovirus, adenovirus, and human metapneumovirus can also be responsible. RSV spreads through respiratory droplets and is highly contagious.
Symptoms:
The hallmark symptom of bronchiolitis is difficulty breathing, characterized by wheezing, rapid breathing, and sometimes a rattling sound in the chest. Other symptoms may include coughing, fever, nasal congestion, and reduced appetite.
Treatment:
Treatment for bronchiolitis is usually supportive and focuses on relieving symptoms. This may include providing supplemental oxygen, ensuring adequate hydration, using nasal saline drops to clear nasal passages, and in severe cases, hospitalization for close monitoring and respiratory support. There is no specific antiviral medication for RSV, but in certain cases, a medication called palivizumab may be prescribed to prevent severe RSV infections in high-risk infants.
Conclusion:
While both bronchitis and bronchiolitis affect the respiratory system, they differ in terms of their causes, demographics affected, and treatments. Understanding these distinctions is essential for healthcare providers, parents, and individuals to effectively manage these respiratory infections and prevent complications. If you or your child experience symptoms suggestive of bronchitis or bronchiolitis, it is important to seek medical advice for proper evaluation and management.

.webp)